

William Fletcher Davis was
born on 21 January, 1917 in Newport News. His parents were Fletcher Allen Davis
and Lora Elizabeth (Roberts) Davis. In 1930, the Davis' lived at 319 36th Street,
Newport News. Fletcher and Lora had 9 children in 1930, Catherine Elizabeth
Davis, Lora Annie Isabell Davis, William Fletcher Davis, Herbert Allen Davis,
Grace Florence Davis (born August 30, 1920), George Richard Davis, Floyd Cain
Davis (born August 3, 1925), Charles Andrew Lindberg Davis, Emily May Josephine
Davis, William was the third oldest and the oldest son. Fletcher Allen Davis
worked at the Shipyard as an electrician.
William apparently worked
at the Shipyard as a ship fitter before he joined the Army.
He joined the Army on July 18, 1940, when Hitler´s war machine was hectoring Europe and more than a year before a Japanese armada attacked Pearl Harbor. A few years later on some battlefield in the Netherlands, Pvt. William F. Davis fell. He died on Oct. 14, 1944. Maybe he was fatally wounded the month before, when Operation Market Garden began and Allied troops made the largest airborne landing in history - falling from the sky, some said, like shooting stars - to try to take key bridges into Germany and end the war by Christmas.
Maybe it was afterward. A sniper. A land mine. One more firefight on a long, terrible slog toward Berlin.
His brother Herbert Allen Davis was born February 7, 1919, Newport News, VA, and died in 1945, possibly also in WWII.
In 1947, William was listed in the Gold Star Honor Roll of Virginians in the Second World War.
His name can also be found on a plaque in the Shipyard along with other employees who died during active duty in WWII. His name is memorialized on the NN Victory Arch along with other Peninsula residents who paid the ultimate sacrifice during that conflict.
 |
 |
|
Newport
News Victory Arch |
Memorial
plaque with name of William Fletcher Davis |
In 1942, the 82nd Infantry Division at Camp Claiborne, LA was split in two, to form two new Airborne Infantry Divisions. The 82nd Airborne and 101ste airborne division. Both divisions were stationed at Ft Bragg, N.C. before being shipped overseas. The 82nd departed first, heading to North Africa. The 101st absorbed one parachute regiment, the 502nd, which had been originally activated as a battalion in 1941. This became the original Parachute Infantry Regiment (PIR) on the Table of Organizations & Equipment (TO&E) of the 101st Division. The division's original organic units were artillery and support battalions. In early 1943, the 506th PIR was attached to the division, which sailed for the UK in September aboard 3 different transport ships. A period of intense maneuvering and training, including practice jumps, ensued in England. The division was preparing for a landing on the Nazi occupied European continent, but the exact location was still unknown. The 501st PIR, which like the 506th, had initially trained seperately, was also attached to the 101st Division in January, 1944, in England. Although both regiments wore the 101st Airborne shoulder patch in battle, the 501st and 506th were only members by attachment until after WW2 ended. The 506th was accepted as a TO&E part of the division after VE-Day.
 |
 |
Patch
of the 101st Airborne Division |
Patch
of the 501st PIR |
The 501st was deactivated in July, 1945, having never been an official organic part of the division. When the 101st was reactivated in 1956, the 501st was incorporated as part of the TO&E. In the spring of 1944, General Bill Lee, the original commanding general of the 101st Airborne had to relinquish command due to a heart ailment. His replacement was General Maxwell D. Taylor, who would lead the 101st through combat until the end of WW2. The 101st participated in Exercise Tiger at Slapton Sands on the south coast of England in April. In June, the Division landed in Normandy on, and behind the Utah Beach area. Paratroopers were dropped onto three landing zones, and relatively few troops of the 101st landed by glider. The rest of the division landed by sea. The three parachute regiments captured the four elevated roads leading inland from Utah Beach and secured various key terrain objectives behind the east coast of the Cotentin Peninsula. This was done with great success, and a new objective was added to their agenda: the taking of Carentan, France. This not only aided in linking the Utah and Omaha beachheads, it helped prevent the Germans from driving through to the coast in an area which would divide the Allied landings. The 502nd 3rd battalion won particular honors in it's costly battle to secure the road into Carentan from the north-this became known as 'Purple Heart Lane', due to the many American casualties taken there. A Congressional Medal of Honor (CMH) was awarded to LTC Robert Cole for his leadership in a bayonet charge at the south end of the causeway. This was the first of only two CMH's awarded to 101st personnel in WW2. The 101st took Carentan and the 506th, reinforced by CCA, 2nd Armored Division, defended it against counterattacks by the 17th SS division and the 6th Para Regiment. The 101st was withdrawn from the lines in late June and sailed back to England on LSTs in July. After several false alerts, they invaded by air again in the Netherlands on 17 September 17, 1944. Their mission in Holland was to hold open a corridor for British armor to drive north and relieve their paratroops who had landed at Arnhem. Although the mission failed to achieve it's long range objectives, the 101st as well as the 82nd Airborne Division accomplished all missions assigned to them. Once again, fierce fighting raged and another 101st man won the CMH. Pfc Joe Mann of H/502 laid on a German grenade to save his buddies; the CMH was awarded posthumously.
 |
Airborne
drop at operation Market Garden |
Withdrawn from Holland
at the end of November for recuperation, the 101st was sent to Camp Mourmelon
le Grand, France. Less than 3 weeks later, the 101st was rushed north into Belgium
in trucks, to counter the German Ardennes counteroffensive. Throwing a cordon
around the key road and rail center of Bastogne, the 101st Division was surrounded
for a week by elements of eight German divisions, but refused to yield the town
to the enemy. Here, General Anthony McAuliffe, the acting commander rejected
a German surrender ultimatum with a one word reply of "Nuts". The
German ring around Bastogne was broken on 26 December, 1944, when elements of
Patton's 3rd Army shot their way into the town. But even heavier fighting ensued,
as the 101st pushed north toward Houffalize for the first half of January, to
help close the Bulge. The 101st left Bastogne in trucks in mid January, 1945,
and the weary Bastogne survivors were rushed to the 7th Army front in Alsace-Lorraine,
to reinforce the line along the Moder River. A month later, the 101st boarded
trains (40&8 boxcars) and returned to the Reims, France area, this time
Mourmelon le Petit, where they received a Presidential Unit Citation for their
defense of Bastogne. In April, the division, minus the 501 PIR, boarded trucks
and went to the Dusseldorf area. The Ruhr Pocket was closed by numerous American
units, trapping most of the German 15th Army. Elements of the 101st rode in
DUKWs to Bavaria to check out the possibility that Hitler had established an
Alpine Redoubt for continued resistance.
This proved to be an overestimated
threat, but elements of the 101st participated in the capture of Hitler's Obersalzberg
complex. Elements of the divison were sent from Berchtesgaden down into Austria,
shortly after VE Day, where they held towns from Krimml to Taxenbach, as occupation
forces. Despite rumors that the division would be rotated to fight in the Pacific
Theatre, the war ended in August. When it was decided that the 101st would be
inactivated and the 82nd retained as a postwar airborne division, the 101st
lost its chance to march in the New York victory parade. By the time the victory
parade took place in early 1946, most survivors of the heaviest fighting were
already discharged under the 'points' system. They had been back working at
civilian jobs for months. Some former Screaming Eagles (mostly rookies) were
among the 82nd Airborne troopers who marched down 5th Avenue. The 101st Airborne
Division was deactivated in late 1945, and ceased to exist as a U.S. Army unit
until it was reborn in 1956. It has continued ever since, with combat tours
in Vietnam and the Gulf War.
In 2001 the television series Band of Brothers came out, this serie is about
E-Co, 506de PIR during the war and gave a boost to the fame of the 101st Airborne
Division.
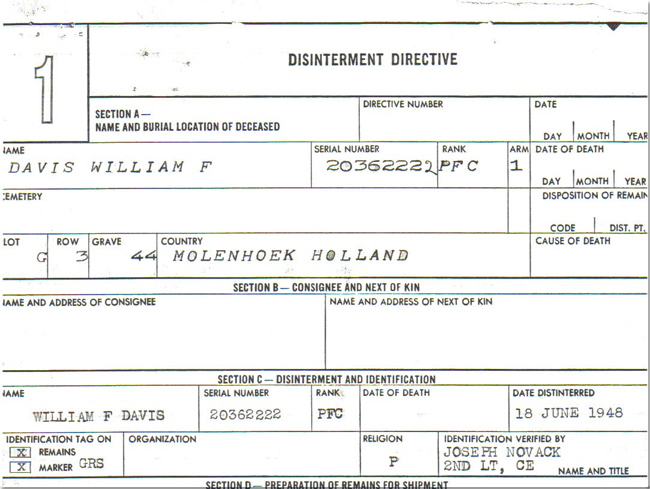
According to a disinterment directive William Fletcher Davis was at first buried at the temporary cemetery at Molenhoek before he was reinterred at the Margraten cemetery in 1948
 |
 |
 |
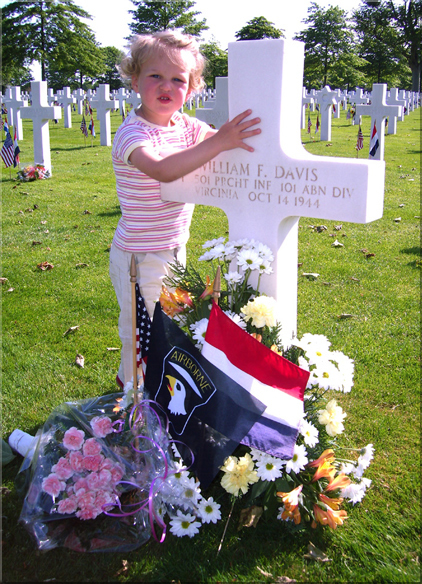 |
A
view of the Margraten cemetery |
caretaker
John Smeets´ daughter Janne at the grave of Pfc William F. Davis |
 |
|
A special word of gratitude for sharing information is going out to : Mr. John Smeets, caretaker of Pfc William F. Davis´ gravesite Mrs. Tamara Dietrich, who works and writes for the Daily Press Mr. Dick Hoffeditz, Curator, Virginia War Museum Mrs. Diane Miller
Lassitter, daughter of 1st Lt. Merritt S. Miller, MIA B25G Pilot
-- off Ponape in Pacific
|